Real-Time Analytics in Race Pace Management
How top F1 teams use real-time telemetry, AI and cloud simulations to optimize pit timing, tire strategy and lap pace within split-second decision windows.

Formula One teams rely on real-time data and simulations to make critical race-day decisions. From tire wear to fuel usage, advanced analytics help teams optimize strategies in seconds. Here's how top teams leverage cutting-edge tools:
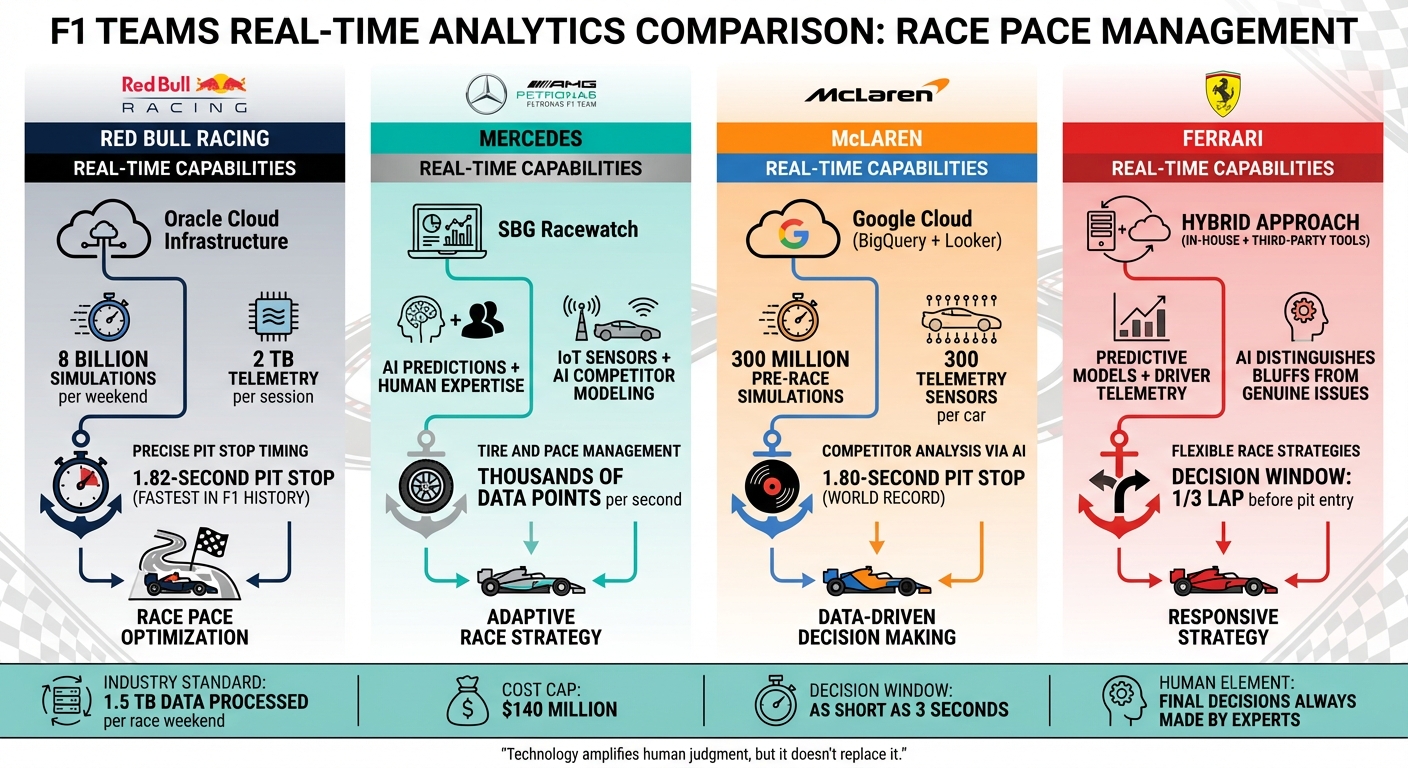
- Red Bull Racing: Runs 8 billion simulations per weekend using Oracle Cloud Infrastructure, enabling precise pit stop timing and rapid decision-making.
- Mercedes: Uses SBG Racewatch for real-time data integration, blending AI predictions with human expertise for tire and pace management.
- McLaren: Processes 250 million data points per race with Google Cloud tools, using AI for competitor analysis and strategy refinement.
- Ferrari: Combines in-house systems with third-party tools for flexible race strategies, focusing on predictive models and driver telemetry.
Teams must process terabytes of data and act within seconds to stay competitive. While AI plays a key role, human judgment remains irreplaceable in final decisions. Success hinges on translating data into quick, informed actions, blending technology and intuition for on-track performance.
F1 Teams Real-Time Analytics Comparison: Data Processing Capabilities
1. Red Bull Racing
Real-Time Data Tools
Red Bull Racing handles an enormous amount of data during every race weekend. Each car generates a staggering 2 TB of telemetry per session, while nearly 4 billion Monte Carlo simulations are run before the race - and billions more during the event itself. To manage this workload, the team relies on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI).
Their setup involves a dual-location strategy: engineers at the pit wall work in tandem with an Operations Room based in Milton Keynes, England. This constant flow of analysis and decision support is crucial for adapting race strategies on the fly. On-car sensors track hundreds of variables, monitoring everything from tire and brake temperatures to G-forces and engine performance.
"Every pit stop call, every strategy decision that has allowed Max Verstappen to win world championships since 2021, has been made on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure." – Jack Harington, Partnership Group Lead, Oracle Red Bull Racing
These tools provide the foundation for making split-second decisions that can define the outcome of a race.
Pace Adjustment Examples
Red Bull's ability to make data-driven decisions has led to some of the most memorable moments in racing. Take the French Grand Prix in June 2021, for example. With 20 laps to go and an 18-second gap to close, Head of Race Strategy Will Courtenay called Max Verstappen in for a second pit stop. The decision, based on data showing fresher tires would make the difference, paid off when Verstappen reclaimed the lead with less than two laps to spare.
Another standout moment came during the Brazilian Grand Prix in November 2019. Senior Strategy Engineer Hannah Schmitz made a bold call to pit Verstappen from the lead during a safety car period, sacrificing track position for the advantage of fresh tires. Similarly, at the Chinese Grand Prix in April 2018, Courtenay executed a "double-stack" pit stop for both drivers under a safety car. This move allowed Daniel Ricciardo to storm past the competition and take the win.
Latency Reduction
Timing is everything in Formula 1. Red Bull's strategists must make decisions within a third-of-a-lap window before a car reaches the pit lane. Thanks to OCI, the team can run about 20% more simulations compared to traditional on-premise systems, giving them a broader set of scenarios to evaluate in less time. While AI models assist by analyzing regulations and historical data, the final calls are always made by human experts.
Red Bull's focus on precision extends beyond strategy to execution. The team set the record for the fastest pit stop in Formula 1 history, changing all four tires in an astonishing 1.82 seconds during the 2019 Brazilian Grand Prix. This achievement highlights how their real-time analytics enhance every aspect of their performance.
2. Mercedes
Real-Time Data Tools
Mercedes-AMG Petronas uses SBG Racewatch as its go-to software for analyzing races in real time. This platform combines telemetry, video streams, and timing data into a single, low-latency interface that engineers can access both at the track and back at the factory. During a race, it processes thousands of data points every second, enabling strategists to quickly refine degradation models and update weather predictions. This seamless integration of data keeps the team ahead in the fast-paced world of Formula 1.
Their advanced simulators take things further by blending historical data with live inputs to predict how the car will react to weather changes or setup tweaks. At the same time, IoT sensors keep tabs on critical car components, helping the team decide when to call for a pit stop or adjust the car's pace. Mercedes also employs AI-driven competitor modeling, which builds profiles of rival teams' strategies, allowing them to anticipate and counter their moves.
"We wish to measure and optimize every aspect of how our engineers and drivers operate across multiple time zones, as well as how we manage a large number of off-car devices and equipment to give us the best chance of on-track success." – James Allison, Technical Director of Mercedes
Pace Adjustment Examples
Mercedes showcased the power of real-time data during the Monza Grand Prix. Strategists noticed through live telemetry that Lewis Hamilton's lap times on aging tires were falling short of the strategy's goals. Meanwhile, his competitors had already pitted. The data made it clear that staying out would cost him track position, leading to an immediate pit call. This quick decision helped protect his position in the race.
Latency Reduction
Mercedes also focuses on minimizing delays in decision-making during races. The team uses dedicated intercom channels for strategy discussions, ensuring that engineers can share live updates and plan contingencies as the race unfolds. The Racewatch platform consolidates all incoming data into a single, low-latency stream, giving both trackside and factory engineers a real-time view of the race. This setup allows the team to act swiftly, often making critical decisions in the brief moments before a driver reaches the pit lane. Despite relying on rapid AI analysis, Mercedes maintains a "human-in-the-loop" approach, where seasoned strategists have the final say.
Basics of F1 Race Strategy
3. McLaren
After exploring the sophisticated data strategies of Red Bull and Mercedes, McLaren's approach stands out with its own flair. The team relies on a real-time data infrastructure to fine-tune race pace management during a Grand Prix. Each car is equipped with 300 telemetry sensors that track over 100,000 parameters, generating a staggering 250 million data points per race and more than 11.8 billion data points over an entire season. To handle this massive influx, McLaren processes around 1.5 terabytes of race data trackside using mobile 38U server cabinets before sending it to the McLaren Technology Centre.
McLaren has teamed up with Google Cloud to manage these enormous datasets. They use BigQuery for data hosting and Looker for real-time visualization. On top of that, the team employs Alteryx, an analytics automation platform, to unify data from wind tunnel tests, computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulations, and live telemetry. Before each Grand Prix weekend, McLaren runs about 300 million race simulations. These simulations are continuously updated during races, allowing for real-time strategy adjustments in decision windows as short as three seconds.
The team also uses AI-powered tools to analyze competitor radio traffic. By applying speech-to-text and sentiment analysis, McLaren gains insights into rival teams' strategies, adding an extra layer of intelligence to their decision-making.
Their data-driven approach has delivered tangible results. At the May 2024 Miami Grand Prix, McLaren's real-time simulations helped Lando Norris extend his tire stint by over 20 laps. This move allowed him to take advantage of a safety car period, ultimately leading to his first Grand Prix victory. Another standout moment came during the October 2023 Qatar Grand Prix, where analytics automation played a key role in achieving a world-record 1.80-second pit stop. This lightning-fast stop helped Norris climb from 10th on the grid to secure a podium finish.
4. Ferrari
Ferrari, like its competitors, uses advanced analytics to stay ahead, but with a unique twist: a hybrid strategy that combines their in-house systems with third-party tools. This approach helps them manage race pace with precision. During a Grand Prix, Ferrari relies on predictive models to simulate thousands of scenarios, identifying the best pit stop windows and backup plans based on live data like tire wear and gaps to competitors. Engineers also keep a close eye on driver telemetry - things like throttle usage and braking patterns - offering real-time feedback to help drivers tweak their style for better performance.
Real-Time Data Tools
Ferrari's "digital pit wall" is a powerful tool, capable of making pit stop decisions within one-third of a lap before the car reaches the pit entry. It uses AI to analyze rival strategies in real time, determining whether an early pit stop by a competitor is a bluff or a genuine issue. Predictive simulations also allow the team to anticipate undercuts and tire compound changes before they happen. Unlike teams that rely solely on exclusive cloud partnerships, Ferrari blends its in-house analytics with third-party tools, creating a flexible system that can adapt strategies mid-race.
Pace Adjustment Examples
Ferrari's ability to fine-tune strategies was evident during the February 2025 Bahrain Pre-Season Testing. Simulations helped the team identify target lap times to reduce tire wear on C2 and C3 compounds, matching Red Bull's consistency while managing thermal degradation. Similarly, during the October 2025 Mexico City Grand Prix practice sessions, overnight telemetry flagged mechanical adjustments needed to improve balance during long runs. Both Charles Leclerc and Carlos Sainz reviewed the data to address an overly "open" car balance caused by the high altitude. Sainz emphasized the importance of refining setup parameters to get more out of the tires over the race distance.
Race Impact
Ferrari's agile analytics allow them to quickly adjust tire degradation forecasts when conditions change, such as a sudden drop in track temperature. At the 2025 Abu Dhabi Grand Prix, the team executed a split tire strategy: Carlos Sainz started on Hard tires from 16th, while Charles Leclerc began on Mediums from 19th. This strategy reflected careful planning, as Leclerc had only one new set of Hards and one new set of Mediums, compared to McLaren's two new sets of Hards per driver. Another example of Ferrari's adaptability came during the 2025 Qatar Grand Prix, where Sainz secured a podium finish by expertly navigating safety car windows, demonstrating the team's ability to make smart, dynamic decisions under pressure.
Pros and Cons
Each Formula 1 team's approach to real-time analytics brings unique strengths and weaknesses that directly influence their performance on race day. By examining these, we can see why some teams excel in specific scenarios while grappling with distinct challenges.
| Team | Key Strengths | Notable Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|
| Red Bull Racing | - Executes up to 8 billion simulations per weekend using Oracle Cloud Infrastructure, allowing them to evaluate nearly every possible race scenario. - Achieved a record-breaking 1.82-second pit stop through data-driven crew performance analysis. |
- Heavy reliance on computational resources makes them vulnerable to cloud latency or system failures. - Dependence on "ghost strategies" to predict rival moves adds a layer of risk. |
| Mercedes | - Employs advanced forecasting models, such as deep learning and XGBoost, to predict critical tire performance drops (known as the "cliff"). - Maintains a strong collaboration between human intuition and AI, allowing engineers to override model outputs when necessary. |
- Striking the right balance between AI predictions and human judgment is tricky and could lead to missed opportunities if instinctual factors are undervalued. |
| McLaren | - Runs approximately 300 million simulations ahead of each race. - Uses sentiment analysis of competitor radio communications for strategic insights. - Leverages Google Cloud tools like BigQuery and Looker for rapid probabilistic modeling. |
- Demonstrated risk aversion under pressure; for example, a delayed pit stop at the December 2025 Qatar Grand Prix cost Oscar Piastri a potential victory. - Decision windows as short as 3 seconds create intense pressure. |
| Ferrari | - Combines proprietary in-house analytics with third-party tools for a flexible hybrid approach. - Uses AI to distinguish genuine issues from strategic bluffs by rivals. |
- Lacks transparency about its specific AI/ML capabilities, making it harder to gauge their full potential. - Faces challenges in balancing traditional racing intuition with fast-paced, machine-driven analysis. |
While simulation and sensor data play a crucial role, financial constraints pose additional hurdles. With a $140 million cost cap and the need to process 1.5 terabytes of data during a race weekend, teams must carefully allocate resources between computational investments and on-track performance.
"In Formula 1, the most important sensor is the driver. Technology amplifies human judgment, but it doesn't replace it."
- Jack Harington, Partnership Group Lead, Oracle Red Bull Racing
Conclusion
The data tells a compelling story: Red Bull Racing harnesses Oracle Cloud Infrastructure to power up to 8 billion simulations per race weekend, enabling rapid decision-making across countless scenarios. Meanwhile, McLaren demonstrates that precision and strategy can outshine sheer computational might. Their 300 million simulations, combined with Google Cloud's BigQuery and Looker, paved the way for a perfectly executed long first stint at the May 2024 Miami Grand Prix, delivering Lando Norris his first win. Mercedes leans heavily on human expertise, utilizing tools like Racewatch and SAP Cloud ERP to support their approach. Ferrari, on the other hand, strikes a balance by integrating proprietary analytics with third-party tools, offering them a flexible edge.
These strategies highlight a crucial point: races aren't won by numbers alone. Victory comes from the ability to translate data into quick, informed actions. Simulation power is only as effective as the decisions it enables.
"AI doesn't decide for us, it informs the human decision. In Formula 1, the most important sensor is the driver. Technology amplifies human judgement, but it doesn't replace it." - Jack Harington, Partnership Group Lead, Oracle Red Bull Racing
The formula for success lies in combining cutting-edge technology with human intuition. Teams that can process massive amounts of data and act on it within split-second windows consistently rise to the top. This fusion of real-time analytics and strategic execution is what turns data into a winning advantage on the track.
FAQs
How do F1 teams use real-time data to make race-day decisions?
Formula 1 teams depend on real-time data to make crucial decisions during a race. Each car is outfitted with over 300 sensors, generating more than 1.1 million data points every second for engineers to analyze. This constant stream of information covers key metrics like tire wear, fuel levels, brake temperatures, and even the driver's vitals. With the help of advanced AI models and simulations, this data is processed on the spot to anticipate tire wear, fuel usage, and the best race strategies.
These real-time insights guide teams in determining the perfect timing for pit stops, adapting strategies to shifting conditions, and responding to unexpected events like weather changes or the appearance of a safety car. By running thousands of live simulations, teams can pinpoint the exact lap for a pit stop or select the most effective tire compound for the moment. This data-driven approach transforms raw telemetry into actionable strategies, often making the difference between winning and losing a Grand Prix.
How do Formula 1 teams use AI to make strategic decisions during a race?
Artificial intelligence has become a game-changer for Formula 1 teams, enabling them to make lightning-fast strategic decisions during races. Each car is equipped with hundreds of sensors that generate millions of telemetry data points every second. These sensors monitor everything from tire wear and fuel levels to brake temperatures and even the driver’s vitals. Using machine learning, this massive stream of data is analyzed in real time to predict critical factors like tire degradation, the best times for pit stops, and fuel management strategies. The result? Teams gain an edge that can make all the difference on race day.
AI doesn’t stop there - it also drives advanced simulations that run thousands of "what-if" scenarios during the race. These simulations help teams assess the impact of unexpected events, like a safety car entering the track or sudden weather shifts. Acting as a real-time strategist, AI sifts through enormous amounts of data to deliver clear, actionable insights. This allows teams to adjust their tactics on the fly and make precise decisions under pressure. In modern Formula 1, AI isn’t just helpful - it’s a critical factor that often separates championship contenders from the rest of the pack.
How do F1 teams combine real-time data and human judgment during a race?
Formula 1 teams depend on a powerful combination of advanced data analytics and human expertise to make crucial decisions in the heat of a race. Using state-of-the-art telemetry systems, they capture over a million data points every second. These data points reveal critical insights about tire wear, fuel levels, and engine performance. The information is processed in real-time to create predictive models that guide strategies like when to pit or which tires to use.
But data isn't the whole story. Drivers play a critical role by sharing real-time feedback on grip, balance, and track conditions. Meanwhile, seasoned engineers weigh in with their understanding of factors like weather changes, safety cars, and the unique characteristics of each circuit. Together, they interpret the data, tweak strategies, and even override algorithm-driven recommendations when the race takes an unexpected turn. This dynamic mix of cutting-edge tech and human judgment allows teams to stay agile and get the most out of their performance on race day.