Top Tools for Fuel Data Analysis in F1
Explore the essential tools and strategies F1 teams use for fuel data analysis to optimize performance and adapt to race conditions.

Fuel data analysis is a critical part of Formula One racing, directly influencing team strategies and outcomes. Teams rely on advanced tools to monitor and optimize fuel consumption in real time, factoring in variables like weather, track conditions, and car performance. Here's a quick overview of the top tools used in F1 for fuel analysis:
- ATLAS by McLaren Applied Technologies: Tracks real-time telemetry and integrates fuel data with environmental factors for precise predictions.
- AWS F1 Insights: Uses cloud computing and machine learning to provide adaptive fuel strategies during races.
- PI-tool: Focuses on high-speed data collection and AI-driven recommendations for fuel efficiency.
- AVL CRUISE: A simulation platform for pre-race fuel modeling and strategy planning.
- MATLAB & Python: Custom-built analytics solutions for flexible and detailed fuel consumption analysis.
- TracingInsights.com: Offers browser-based tools for interactive fuel correction and lap time comparisons.
- Real-Time Telemetry Systems: Provides live data streams for immediate strategy adjustments.
- Fuel-Corrected Lap Time Analytics: Normalizes lap times by accounting for fuel weight, offering clearer performance insights.
- Simulation and Scenario Modeling Tools: Predict fuel usage under various conditions using historical and live data.
- Track Condition and Weather Data Integration: Combines weather and track data to refine fuel strategies dynamically.
These tools enable teams to make informed decisions, simulate race scenarios, and adjust strategies on the fly to maximize performance. Below is a quick comparison chart summarizing their capabilities.
Quick Comparison
| Tool | Real-Time Data | Predictive Models | Weather Integration | Key Feature |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ATLAS | Yes | Yes | Yes | Detailed telemetry dashboards |
| AWS F1 Insights | Yes | Yes (ML-based) | Yes | Multi-car data analysis |
| PI-tool | Yes | Yes | Yes | AI-driven recommendations |
| AVL CRUISE | Limited | Yes (simulation) | Yes | Pre-race fuel modeling |
| MATLAB & Python | Yes (custom) | Yes (flexible) | Yes | Custom analytics workflows |
| TracingInsights.com | Limited | Limited | Yes | Interactive lap comparisons |
| Real-Time Telemetry Systems | Yes | No | Yes | Live race-day adjustments |
| Fuel-Corrected Lap Time Analytics | Limited | Limited | Yes | Normalized lap performance |
| Simulation and Scenario Modeling | Limited | Yes | Yes | Pre-race scenario planning |
| Track Condition & Weather Data | Yes | Yes | Yes | Dynamic fuel adjustments |
These tools are tailored to meet the demands of F1's fast-paced environment, ensuring every decision is backed by data.
How Do F1 Teams Optimize Fuel With Secret Software? - Pole Position Experts
1. ATLAS by McLaren Applied Technologies
McLaren Applied Technologies created ATLAS, a cutting-edge data platform designed to handle fuel management in Formula 1. This system processes multiple streams of telemetry data at once, delivering precise, real-time insights into fuel usage.
ATLAS monitors key metrics like fuel flow, consumption, and engine efficiency in real time. This gives teams the ability to track fuel usage across different sections of the track and make strategic adjustments mid-race.
What sets ATLAS apart is its ability to combine fuel data with track conditions, such as temperature and other environmental factors. This integration helps teams predict fuel usage with impressive accuracy, even as conditions change, and make smarter strategic decisions.
The platform also uses predictive modeling to estimate fuel needs under various scenarios. Teams can simulate different fuel loads to find the best balance between performance and fuel efficiency. These predictions are made even more accessible through ATLAS's user-friendly visualization tools.
The system provides race engineers with clear and intuitive dashboards. These include graphs and track maps that highlight fuel consumption trends, making it easier to spot potential issues quickly.
To round out its capabilities, ATLAS incorporates weather data and tire performance metrics, offering a more complete picture of race dynamics. Its AI-driven features also improve fuel consumption forecasts over time, keeping teams ahead of the curve.
2. AWS F1 Insights
Amazon Web Services brings a powerful tool to the racing world with AWS F1 Insights - a cloud-based platform designed to provide real-time telemetry analysis, particularly around fuel usage. By processing massive amounts of race data as events unfold, this platform delivers actionable insights to help teams manage fuel consumption effectively.
What sets AWS F1 Insights apart is its ability to adapt fuel management strategies using advanced data integration and machine learning. The platform adjusts fuel predictions in response to changing track conditions, ensuring teams can make informed decisions. Its scalable design also allows for the simultaneous analysis of multiple cars' data during critical race sessions.
Another standout feature is the integration of fuel data with live weather updates. This combination sharpens predictions and enables the use of predictive modeling to simulate various race scenarios. Teams can then optimize both fuel strategies and pit stop timing. While ATLAS focuses on providing comprehensive telemetry data, AWS F1 Insights excels in dynamically adapting strategies for multiple vehicles by incorporating live environmental factors.
3. PI-tool from McLaren Applied Technologies
McLaren Applied Technologies has created a cutting-edge fuel analytics platform, drawing from their deep experience in Formula 1. This tool takes McLaren's renowned expertise to a new level, focusing on fuel optimization through a constant flow of real-time data.
The platform gathers live data from a network of onboard sensors, transmitting it to cloud servers at speeds far surpassing standard telemetry systems. This high-speed data collection is the backbone of its advanced analytical capabilities.
By combining real-time data with predictive modeling and AI-driven recommendations, the system translates raw information into practical insights. During testing, the top 25% of drivers managed to cut fuel and carbon emissions by up to 6.5% and improved cycle times by 5.6%. Broader testing showed a 4.5% reduction in fuel usage when compared to control groups.
These insights allow engineers to spot fuel consumption patterns and anomalies as they happen, improving overall fuel management. Additionally, the platform's predictive models can estimate fuel needs under various conditions, providing valuable input for strategic decisions in fast-changing scenarios.
4. AVL CRUISE
AVL CRUISE is a simulation tool widely used by F1 teams to analyze fuel data. It allows engineers to model fuel consumption under different conditions, helping them make quick, informed strategic decisions.
5. MATLAB & Python-Based Custom Analytics
In the world of advanced analytics, many F1 teams are moving beyond off-the-shelf tools and diving into custom-built solutions. While commercial platforms provide strong capabilities, MATLAB and Python have emerged as go-to programming environments for crafting specialized fuel analysis tools. These custom systems are designed to align with each team's unique methodologies, delivering real-time insights that work seamlessly alongside proprietary systems.
Python, in particular, plays a central role in F1 analytics. Tools like the FastF1 package offer extensive access to race data, including results, telemetry, and weather information. Meanwhile, LiveF1 provides direct access to both live and historical F1 data, making it a valuable resource for custom fuel analysis workflows. FastF1's integration with Pandas allows engineers to work with extended DataFrames, while Matplotlib enables detailed visualizations. This combination is especially useful for analyzing fuel consumption under different track conditions. On the other hand, LiveF1 excels in real-time data processing, empowering teams to create custom pipelines from raw telemetry data.
While Python shines in data handling and real-time processing, MATLAB brings unmatched modeling capabilities to the table. With tools like the Curve Fitting Toolbox and core functions such as fit, plot, interp2, and surf, MATLAB enables precise modeling of fuel consumption patterns. When paired with Simulink, teams can construct lookup tables for optimal engine performance based on Brake Specific Fuel Consumption (BSFC) surfaces, allowing for accurate fuel predictions in various racing scenarios. Beyond fuel analysis, MATLAB's advanced mathematical modeling is also used to study car dynamics, tire wear, and other performance metrics, all while processing real-time telemetry data.
Custom-built solutions offer teams the ability to integrate proprietary algorithms, incorporate unique data sources, and quickly adapt to changes in regulations. By combining Python's strong data processing capabilities with MATLAB's advanced modeling tools, teams create a powerful workflow for fuel consumption predictions and scenario analysis.
6. TracingInsights.com Interactive Analytics
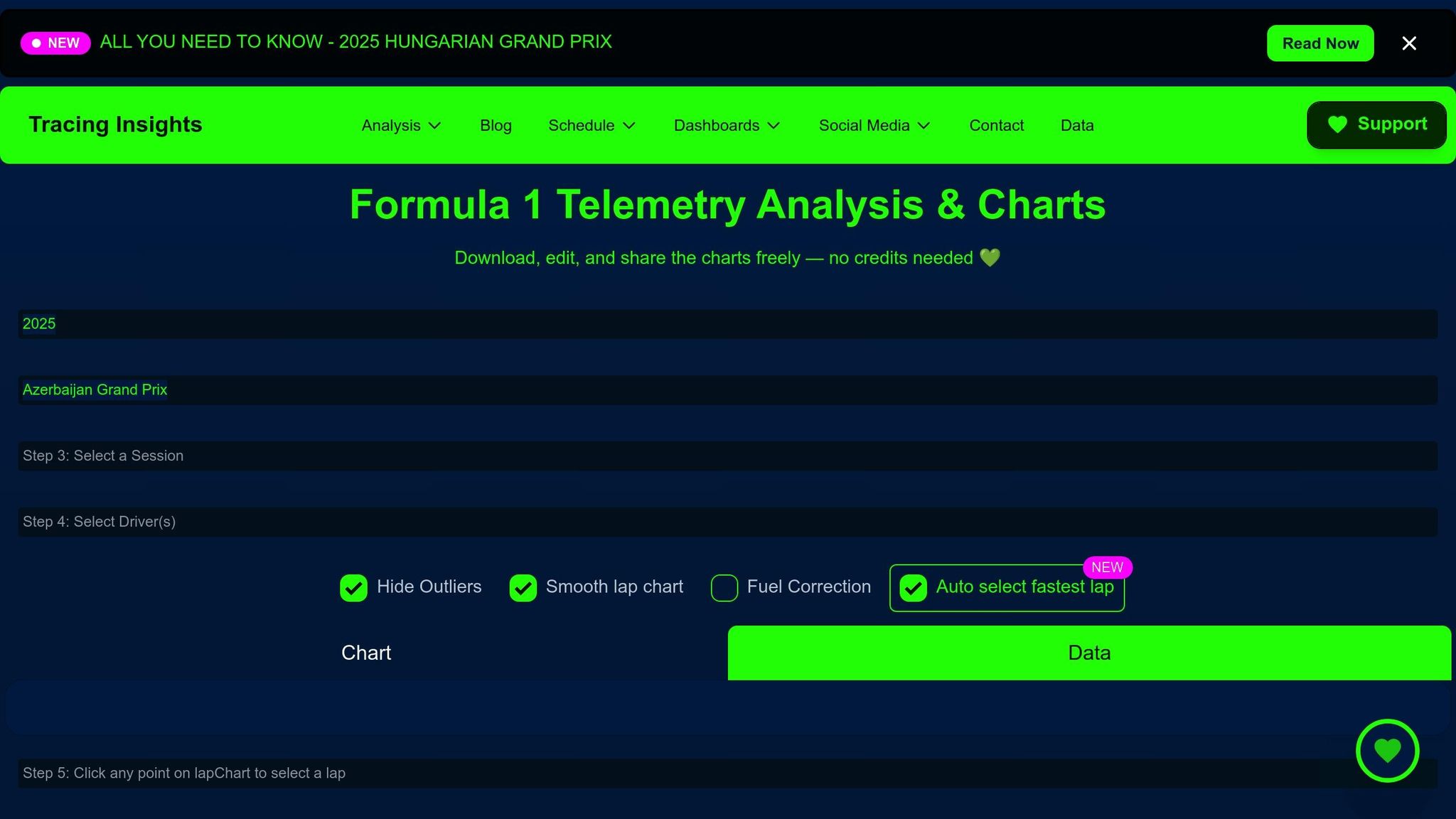
TracingInsights.com is a web-based platform designed to deliver in-depth F1 fuel analysis right in your browser. Its user-friendly interface makes it easier for engineers and strategists to dive into detailed fuel data without unnecessary complexity.
One standout feature is Fuel Correction, which adjusts lap times to account for changes in fuel weight. The platform includes interactive charts where engineers can toggle this fuel correction on or off. This allows teams to compare raw lap times with fuel-corrected ones, providing a clearer view of performance independent of fuel load adjustments.
The platform also combines real-time telemetry with track and ambient weather data. Its Interactive Lap Times Data Table includes track status indicators to reflect race conditions: green for normal conditions, yellow and orange for safety car periods, red for red flags, purple for virtual safety car phases, and cyan for the end of a VSC phase. These visuals provide essential context for understanding how race conditions influence fuel consumption.
Another key feature is the Track Map, which breaks driver performance into 25 mini-sectors. This helps teams link fuel usage to specific sections of the circuit. Paired with detailed telemetry data - like speed, throttle, brake, gear, RPM, acceleration, and track elevation - and a Sector Time Breakdown tool, the platform highlights differences in fuel efficiency across various track segments. Together, these tools offer a comprehensive way to refine race strategies.
7. Real-Time Telemetry Systems
Real-time telemetry systems are the backbone of decision-making during races and practice sessions, capturing and transmitting fuel consumption data as it happens.
By pulling sensor data from the car and environmental sources, these systems give engineers a clear picture of fuel usage. With this information, teams can tweak their strategies on the fly, adapting to changing track conditions or unpredictable weather. It's like having a constant feedback loop that ensures every drop of fuel is used as efficiently as possible.
What makes these systems even more powerful are the advanced visualization tools. They take raw data and turn it into clear, actionable insights, helping teams spot patterns and make performance tweaks that could mean the difference between winning and losing.
In short, real-time telemetry is all about precision and adaptability, showcasing F1's commitment to cutting-edge, data-driven performance.
8. Fuel-Corrected Lap Time Analytics
Fuel-corrected lap time analytics offer a clear view of a Formula One car's true performance by isolating its pace from the effects of fuel weight.
Every kilogram of fuel adds roughly 0.03 seconds to a lap time. For example, with a 110 kg fuel load, a car could be slowed by more than 3 seconds per lap, making accurate adjustments essential.
TracingInsights.com uses a system that accounts for the "Fuel Weight Effect." This involves subtracting the added time - calculated by multiplying the remaining fuel (assuming 100 kg for full races or 30 kg for sprints) by 0.03 seconds per kilogram - from the raw lap time. The result is a normalized lap time that reflects performance as if fuel loads were consistent. This method not only clarifies performance metrics but also provides teams with better tools for strategic planning.
By correcting for fuel weight, teams can identify genuine performance gains rather than those stemming solely from reduced fuel loads. This helps compare drivers across different race stages, analyze setup changes, and evaluate tire wear without the distortion caused by fuel weight.
Experts suggest switching between raw and fuel-corrected lap times to gain insights, particularly during the opening stint of a race, when fuel weight has the largest impact on lap times. The corrected data allows teams to refine strategies for pit stops, tire usage, and driver instructions based on actual performance rather than weight-influenced times.
When combined with broader race strategy tools, fuel-corrected lap time analytics enhance systems like real-time telemetry. They fine-tune fuel and performance strategies by integrating corrected times into predictive models, helping teams forecast race outcomes, determine optimal pit windows, and plan competitive moves throughout the race.
9. Simulation and Scenario Modeling Tools
Simulation and scenario modeling tools play a key role in Formula One fuel analysis, helping teams evaluate countless race scenarios before the actual event. By combining live telemetry, historical performance data, and weather forecasts, these tools provide accurate inputs for predicting fuel consumption. This process helps teams fine-tune both their on-track strategies and fuel management plans.
What makes these tools so effective is their ability to precisely replicate driver behavior and car performance. They take into account factors like driver skills and vehicle metrics, which directly impact fuel efficiency during a race.
Another standout feature is their ability to model environmental conditions dynamically. For example, they factor in temperature changes and rainfall intensity to predict how such variables might influence fuel consumption.
Teams rely on these tools to explore "what-if" scenarios, allowing them to evaluate how different driving strategies or sudden weather changes could affect fuel usage under various race conditions. These tools also simulate tire strategies, revealing how different choices might alter fuel consumption patterns. By running these detailed simulations, teams can optimize their fuel strategies well before race day. When combined with real-time telemetry data, these insights form a comprehensive approach to fuel management.
10. Track Condition and Weather Data Integration
Integrating track condition and weather data has become a game-changer in Formula One fuel analysis. These tools merge various data streams to provide a detailed understanding of how environmental factors influence fuel consumption throughout a race weekend. This approach sets the stage for precise, real-time adjustments as conditions evolve.
At the heart of these systems are real-time weather monitoring tools. By pulling data from multiple sources, teams get up-to-the-minute updates on temperature, humidity, wind speed, and the chance of rain - critical factors that directly impact both car performance and fuel strategies.
Monitoring track surface temperatures is equally essential. Asphalt temperatures can shift significantly during the day, influencing tire grip and rolling resistance, which in turn affects fuel efficiency. Teams use infrared sensors to track these temperature changes across different parts of the track, allowing them to recalibrate fuel strategies on the fly.
Advanced weather radar systems further enhance this integration by predicting rain intensity and duration. This enables teams to adjust their fuel strategies in real time, ensuring they’re prepared for sudden shifts in weather.
These tools don’t work in isolation - they build upon telemetry and simulation data collected earlier. For example, monitoring track grip levels, which can change due to rubber buildup on the racing line, provides additional insight into how the evolving track conditions might affect fuel consumption. Wind data, when integrated, helps fine-tune calculations for aerodynamics and fuel usage.
Behind all these capabilities are sophisticated algorithms that weigh environmental factors based on their impact on fuel consumption. Instead of relying on static calculations, teams can constantly update their fuel estimates as conditions change. This dynamic approach ensures race strategies are more responsive and efficient, giving teams a competitive edge by aligning fuel predictions with real-time environmental data.
Tool Comparison Chart
The chart below outlines the strengths of various fuel data analysis tools across different track and weather conditions. Selecting the right tool depends on specific race-day needs and team goals. Each platform has its own advantages, making it suitable for particular Formula 1 scenarios.
| Tool | Real-Time Capabilities | Predictive Modeling | Track Condition Adaptability | Data Visualization | Best Use Scenarios |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ATLAS by McLaren Applied Technologies | Excellent | Advanced | High | Professional dashboards | Handling diverse weather conditions and strategic planning |
| AWS F1 Insights | Good | Machine learning-based | Moderate | Broadcast-quality graphics | Enhancing fan engagement and post-race analysis |
| PI-tool | Excellent | High-precision algorithms | Very High | Engineering-focused | Optimizing variable weather and tire strategies |
| AVL CRUISE | Moderate | Simulation-heavy | High | Technical charts | Pre-season development and powertrain optimization |
| MATLAB & Python Analytics | Customizable | Highly flexible | Very High | Custom visualizations | Research-focused tasks and algorithm creation |
| TracingInsights.com Interactive Analytics | Good | Standard | Moderate | Interactive web interface | Quick assessments and team briefings |
| Real-Time Telemetry Systems | Excellent | Limited | High | Live data streams | Race day operations and pit wall decision-making |
| Fuel-Corrected Lap Time Analytics | Good | Specialized | Moderate | Performance-focused | Qualifying analysis and pace comparisons |
Choosing the right tool involves balancing precision with strategic flexibility. Race conditions vary widely - from wet tracks that require real-time temperature adjustments to high-altitude circuits that demand atmospheric data integration. Costs also play a role, with options ranging from high-end tools with steep licensing fees to budget-friendly, open-source solutions. Integration capabilities differ too; while some platforms offer seamless data connectivity, others may require manual imports. Many teams opt for a hybrid approach, combining multiple tools to get the best of each. This underscores the importance of tailoring fuel analysis strategies to meet the unique challenges of every race.
Conclusion
The fuel data analysis tools discussed in this guide are reshaping how teams approach race strategy and fuel efficiency. From McLaren Applied Technologies' ATLAS platform to custom analytics built with MATLAB and Python, these tools enable teams to fine-tune efficiency and manage fuel loads effectively.
Real-time telemetry systems, like AWS F1 Insights and AVL CRUISE, give pit wall engineers the ability to monitor fuel consumption instantly and make adjustments before cars even hit the track. Together, these technologies create a robust framework for both race-day decisions and pre-race preparations.
The integration of ERS data from components like MGU-K and MGU-H has also transformed how teams approach fuel efficiency. By capturing energy from braking and exhaust heat, teams can significantly improve fuel usage. This holistic approach reflects the ongoing evolution of F1 strategies covered earlier.
These tools are invaluable for adapting to diverse track conditions. Whether it’s navigating Silverstone’s unpredictable weather or tackling Mexico City’s high-altitude challenges, platforms such as PI-tool and MATLAB-based analytics offer the flexibility needed to adjust fuel strategies on the fly.
For more technical insights into how these data tools influence race outcomes and strategies, check out F1 Briefing. As fuel analysis remains a cornerstone of championship success, these tools continue to shape the competitive edge in modern Formula One.
FAQs
How do F1 teams use real-time weather and track data to refine fuel strategies during a race?
F1 teams use cutting-edge data analysis tools to weave real-time weather and track conditions into their fuel strategies. With the help of telemetry systems and edge computing, they keep a close eye on live metrics like track surface temperature, shifting weather patterns, tire wear, and fuel flow rates. This constant stream of data helps teams fine-tune fuel loads, plan pit stops, and adapt their overall strategy as conditions on the track change.
By processing this information instantly, teams can make precise, informed decisions that boost fuel efficiency and performance - helping them stay competitive, even when race conditions are unpredictable.
Why do F1 teams prefer custom tools like MATLAB and Python for fuel data analysis instead of commercial platforms?
F1 teams often rely on custom tools like MATLAB and Python for fuel data analysis because these tools offer both flexibility and efficiency. MATLAB stands out with its advanced toolboxes and engineering-focused features, making it perfect for handling complex simulations and mathematical modeling. On the other hand, Python’s extensive open-source libraries and seamless integration capabilities allow teams to quickly create and adapt solutions tailored to their specific needs.
By using these custom tools, teams can design workflows that fit their unique requirements, uncover critical insights more quickly, and save money compared to using generic commercial platforms. This level of customization helps them tackle the challenges of changing track conditions and evolving race strategies with precision.
What is fuel-corrected lap time, and how does it help F1 teams during a race?
Fuel-corrected lap time adjusts a car's lap time to factor in the effect of fuel weight, providing a clearer picture of the car's actual performance. This calculation allows teams to evaluate driver performance on an even playing field, refine pit stop strategies, and make better decisions about fuel usage and tire management. By analyzing how fuel loads influence lap times, teams can use this data to make smarter strategic choices and improve their chances of success on race day.