
AR in F1: Behind the Broadcast
How AR and centralized broadcast tech reshape F1: real-time overlays, 3D virtual studios, onboard cameras and the Apple Vision Pro viewing future.

How AR and centralized broadcast tech reshape F1: real-time overlays, 3D virtual studios, onboard cameras and the Apple Vision Pro viewing future.
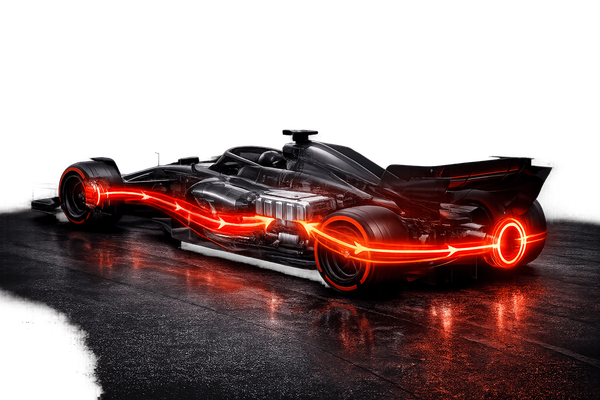

How F1's ERS captures braking and exhaust energy to boost power, shape race strategy and manage fuel and tyre wear — plus the 2026 electrification shift.
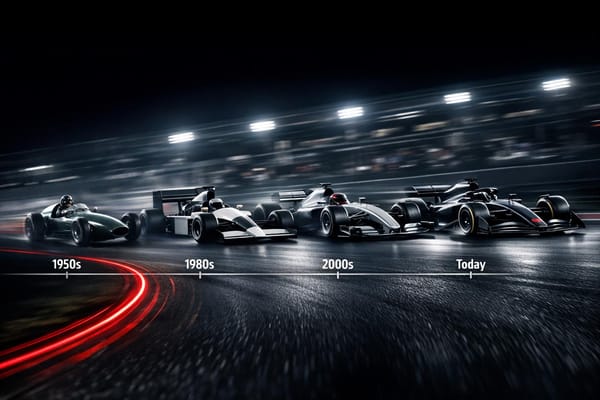

How F1 constructors changed from the 1950s to today — technical revolutions, financial pressures, manufacturer takeovers, and the stabilizing effect of the budget cap.
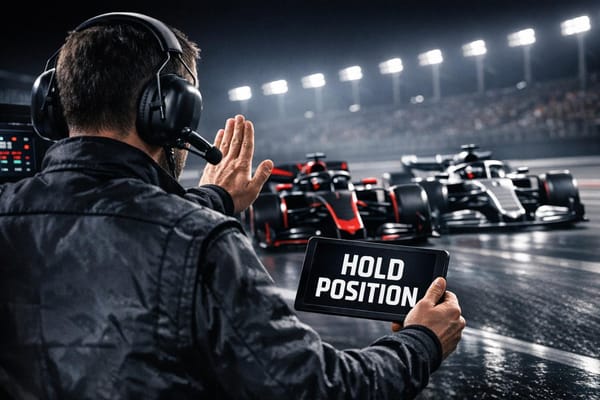

Eight pivotal F1 team orders that reshaped championships, driver rivalries, and team strategy — from Williams and Ferrari to McLaren and Mercedes.
How F1 tires are collected, shredded and transformed into energy, recovered materials and rubberized asphalt—supporting F1's push toward carbon neutrality.

Breaks down an F1 team principal’s role: leading operations, setting race strategy, managing personnel, handling media and FIA politics to drive team performance.
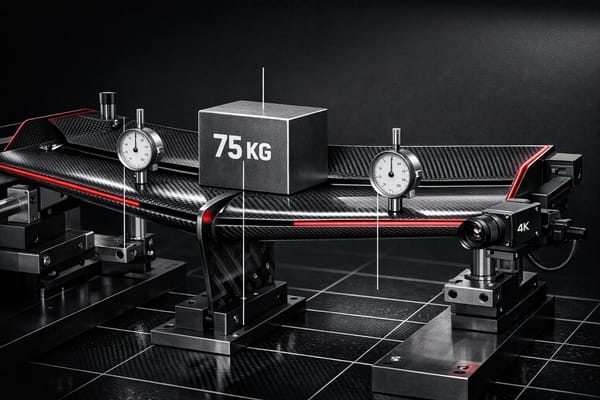

How the FIA enforces rear wing rigidity: 75 kg static load tests, 4K on-track monitoring, tighter slot-gap limits and new 2025 technical directives.

2022 aerodynamic rules reshaped F1: which teams adapted, how drivers adjusted to ground-effect cars, and why overtaking and setups changed the championship.
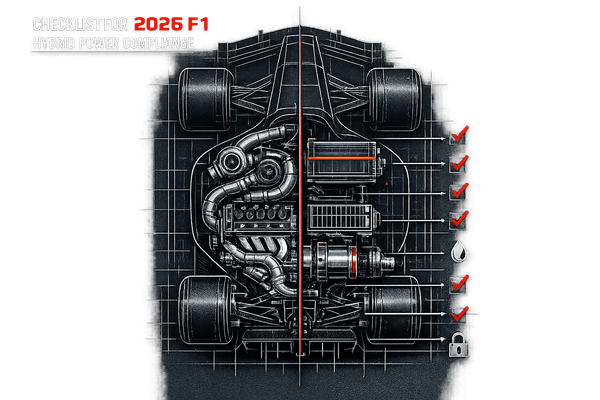
Checklist of 2026 F1 hybrid power rules: 50/50 ICE-electric split, 350 kW MGU-K, MGU-H removal, 100% sustainable fuels, reduced fuel flow, budget and homologation limits.
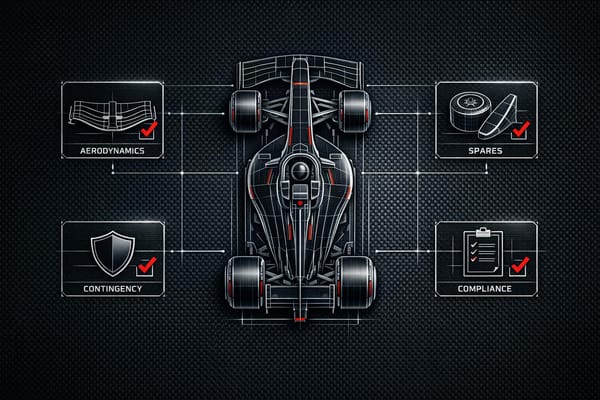
Practical checklist for allocating F1 resources under the 2026 budget cap—prioritize aero upgrades, power-unit efficiency, spares, contingencies, and FIA compliance.

Explore the 1950s rivalry that defined early Formula One—contrasting driving styles, decisive races, head-to-head stats, and lasting influence on the sport.

How blockchain transforms F1 media rights: transparent ownership, smart-contract payments, NFT ticketing, fan tokens and decentralized streaming.
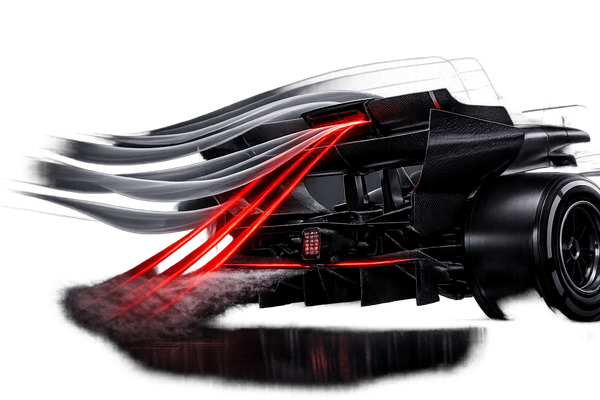

Explains how F1 rear and beam wings generate downforce, how DRS alters airflow (including beam-wing stall and Triple DRS), and what 2026 active aero changes.
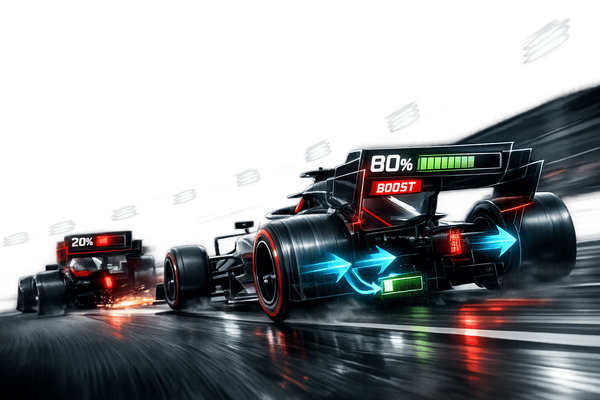

How ERS and Active Aero replace DRS in 2026, adding Boost and Overtake modes that force strategic battery management and change overtaking tactics.
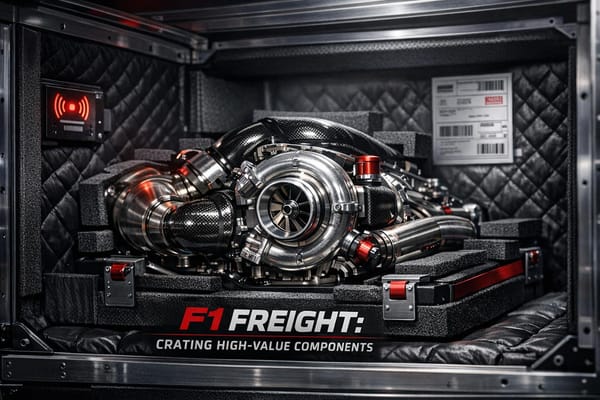

How F1 teams disassemble, crate and ship fragile car parts worldwide using climate-controlled containers, RFID tracking, and multimodal freight.

AWS machine-learning analysis of lap times normalizes car performance to rank the top 10 F1 drivers by raw qualifying speed across eras.

How teams use tire blankets, brake heat, driver techniques and real-time telemetry to keep F1 tires in the 90–110°C range for optimal grip and longevity.

Full-wet F1 tires are advanced but often sidelined by massive spray and a 6–7s pace deficit; Pirelli aims to cut spray and close the wet/intermediate gap by 2026.

Why Ricciardo failed to sync with McLaren's cars: driving-style mismatch, limited testing, ground-effect rules and setup limits that cost lap time.

Move into F1: match transferable skills, tailor your resume, gain motorsport experience, network, and prepare for interviews.

How top F1 teams use real-time telemetry, AI and cloud simulations to optimize pit timing, tire strategy and lap pace within split-second decision windows.

Venturi tunnels and sliding skirts revolutionized F1 aerodynamics, forcing rivals to overhaul chassis, suspension and cooling from 1977 to 1981.

Regional F1 media shape driver reputations—domestic broadcasters favor home drivers, skewing global narratives and sponsorships in a 'wrong passport' effect.

How F1 teams combine hyper-local weather radar, real-time telemetry and ML models to predict tire degradation, optimize pit timing and manage race risk.